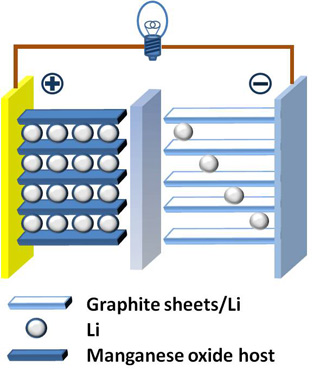
An example of a Lithium-ion battery. Learn more about electrochemical energy storage in Lecture 3. (Image by Chem511grpThinLiBat on Wikimedia Commons.)
Instructor(s)
Prof. Martin Bazant
MIT Course Number
10.626 / 10.426
As Taught In
Spring 2014
Level
Undergraduate / Graduate
Course Description
Course Features
Educator Features
Course Description
This course introduces principles and mathematical models of electrochemical energy conversion and storage. Students study equivalent circuits, thermodynamics, reaction kinetics, transport phenomena, electrostatics, porous media, and phase transformations. In addition, this course includes applications to batteries, fuel cells, supercapacitors, and electrokinetics.


