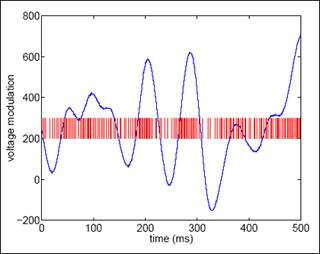
Data from an experiment on the weakly electric fish Eigenmannia. The frequency of action potential firing increases when the stimulus increases. (Image courtesy of Prof. Sebastian Seung from his notes on neural coding: Linear models.)
Instructor(s)
Prof. Sebastian Seung
MIT Course Number
9.29J / 9.912J / 8.261J
As Taught In
Spring 2004
Level
Undergraduate
Course Description
Course Features
Course Description
This course gives a mathematical introduction to neural coding and dynamics. Topics include convolution, correlation, linear systems, game theory, signal detection theory, probability theory, information theory, and reinforcement learning. Applications to neural coding, focusing on the visual system are covered, as well as Hodgkin-Huxley and other related models of neural excitability, stochastic models of ion channels, cable theory, and models of synaptic transmission.
Visit the Seung Lab Web site.
Other Versions
Other OCW Versions
Archived versions: ![]()


